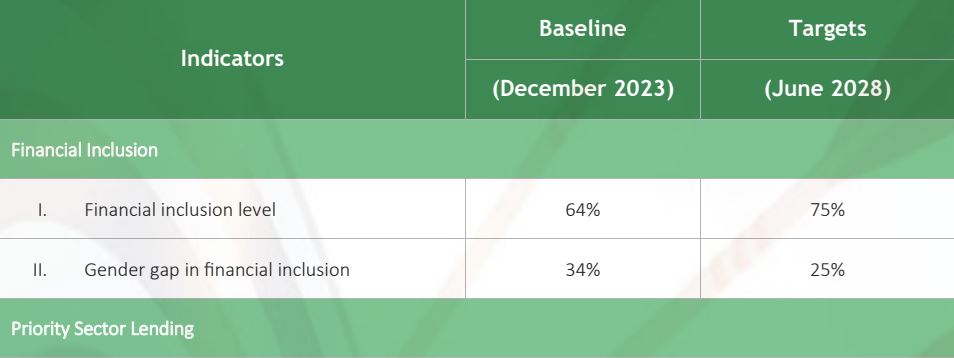
The State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) announced its National Financial Inclusion Strategy (NFIS) for 2024-2028, setting an ambitious target to increase financial inclusion from 64% in 2023 to 75% by 2028 and reduce the gender gap in financial inclusion from 64% to 75% by 2028. 34% in 2023 to 25% in 2028.
The new strategy emphasizes expanding access to financial services in deprived areas, benefiting from digital innovation, and empowering consumers through education and protection.
The National Financial Inclusion Strategy 2024-28 revolves around five strategic objectives to enhance access, use and quality of financial services:
Expanding the availability and use of financial services in disadvantaged and disadvantaged areas
The SBP plans to develop geographic mapping and zoning to identify gaps in financial services. It aims to increase access points, including branches, ATMs and mobile banking agents, with an expansion plan targeting underserved areas.
 Innovative measures include the launch of the Asan Business Account (ABA) to facilitate access to finance for micro and small enterprises (MSEs).
Innovative measures include the launch of the Asan Business Account (ABA) to facilitate access to finance for micro and small enterprises (MSEs).
Promoting safe and easy digital financial services
The main focus is on digital finance, with initiatives such as Raast merchant payments, QR codes, and pseudonym-based payment systems.
The Pakistan Strategic Partnership Program will establish a fintech and innovation center in Karachi, develop an open banking regulatory framework, and operate digital banks to promote financial inclusion.
A pilot project will transform 20 villages into fully digitally enabled ecosystems.
Strengthening the ecosystem for financing priority sectors
Priority sectors such as agriculture, SMEs and housing will receive special attention. The agriculture sector, which contributes about 24% of GDP and employs 37% of the workforce, will benefit from digital land registries, electronic warehouse receipt financing, and partnerships with fintech companies.

SMEs, which currently receive only 6% of total private sector credit, will see initiatives such as scorecard-based financing and digital loan applications.
Strengthening the capabilities and role of financial institutions
The state budget program plans to modernize regulatory frameworks, strengthen microfinance operations, and introduce a youth financial inclusion strategy to support entrepreneurship. Capacity building programs will focus on sectors such as Islamic finance, housing, and sustainable development.
Promoting consumer protection, empowerment and awareness
Recognizing the rise in digital risks, SBP will integrate financial literacy into the national curriculum for grades 1-12 and create a Center of Excellence in Financial Literacy.
A comprehensive consumer protection framework will address issues such as data theft, phishing and over-leverage.
Furthermore, the strategic planning program will develop green housing financing policies and facilitate renewable energy initiatives to promote sustainable development. Partnerships with fintech companies and agricultural service providers aim to create scalable digital solutions for finance.

SBP plans to launch a financial inclusion index and dashboard to monitor progress annually. Surveys and research initiatives will monitor consumer behavior and challenges in accessing financial services to guide future policies.
The strategy prioritizes disadvantaged areas, with plans to bring at least 75% of the population into the formal financial system by 2028. Specific goals include increasing access to digital payments, enhancing financing for small and medium enterprises, and integrating technology into agricultural finance to advance rural communities.
